Improving Mobility, with Knee Replacement
Total Knee Replacement is virtually a “Holy Grail” for
patients crippled with knee arthritis.
The first TKR was performed in 1968. Subsequent innovation, technological advances,
surgical refinement have greatly impacted the efficacy & spectrum of this surgery. Today
approximately 250000 TKRs are performed annually in India.
Total Knee Replacement essentially aims at alleviation of pain,
correction of deformity effectively restore mobility & thus transforming the
Quality of Life for those experiencing
severe knee pain and disability.
However, it is imperative to emphasise that Total Knee Replacement is a
major surgery.
Your healthcare consultant will provide guidance regarding the potential benefits of the
surgery, but ultimately, the decision to proceed rests with you. It is essential to
ensure that your expectations regarding the outcome are realistic and that you have a
clear understanding of the entire process involved. The intention of this article is to
furnish you with sufficient information to make an informed decision.
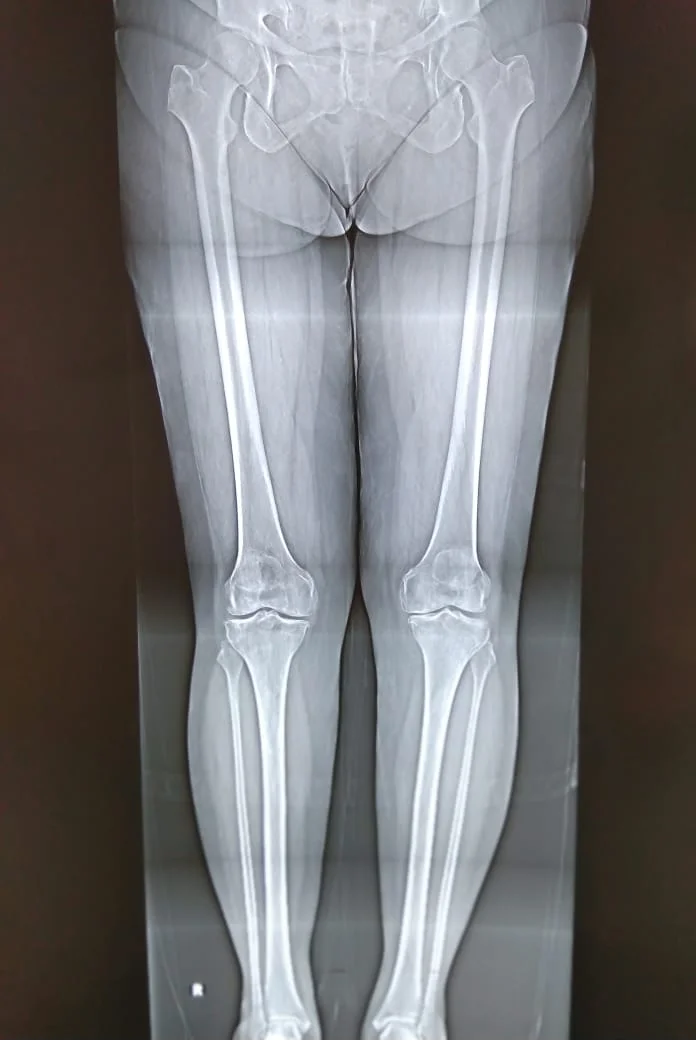
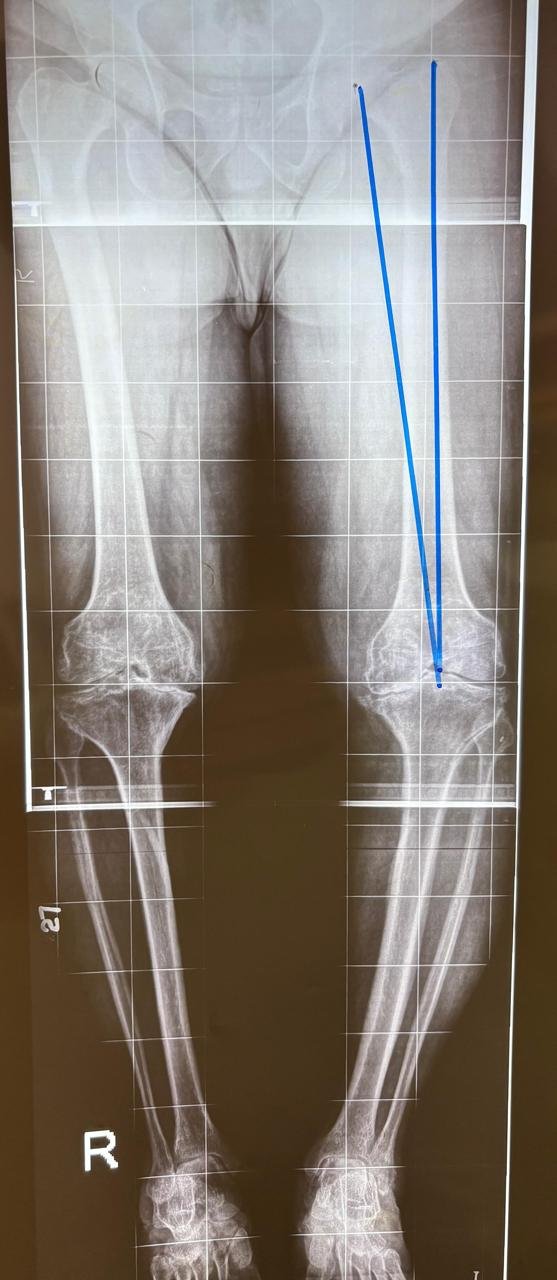
What Are the Most Common Causes of Knee Arthritis?
By far the most common cause, resulting from the degeneration of articular
cartilage. Eburnation causes friction between the bones, leading to pain, stiffness
& deformity.
Autoimmune disease characterised by inflammation in multiple joints. It primarily
affects
women in their middle age (30-40yrs). Early diagnosis is of paramount importance for
prevention of advanced crippling arthritis.
Intra-articular Proximal Tibia & Distal Femoral fractures can lead to secondary
arthritis of
knee due to chondral abrasion & associated articular cartilage damage. Appropriately
indicated HTO can stall but can never prevent development of age related cartilage
degeneration & subsequent arthritis.
- Gout & Crystalline Arthropathy
- SPONK (UKR > TKR)
- Haempophllic Arthropathy & PVNS
Seeking appropriate medical care and making lifestyle changes can help alleviate
symptoms and
improve joint health in these conditions.
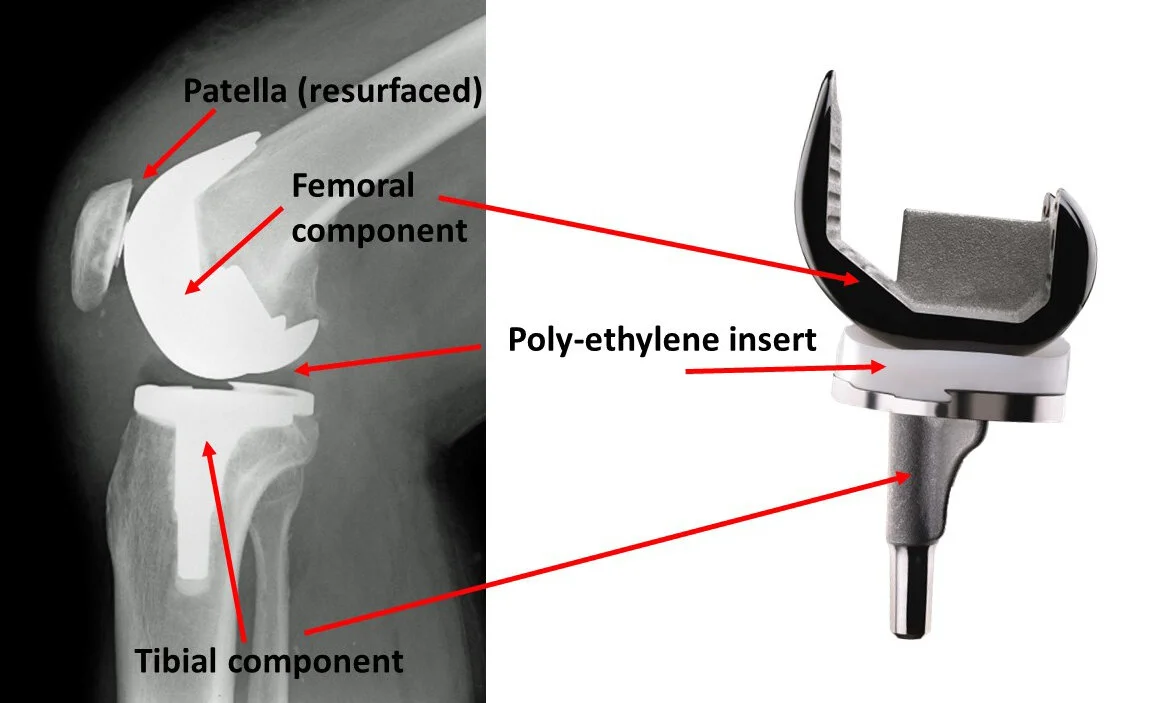
Knee Joint Prosthesis
Cemented Fixed Bearing TKR (PS/CR) is the Gold Standard across the globe.
Factors taken into consideration for knee joint prosthesis include:
- Age & Level of Physical Activity
- Degree of Deformity
- Competence of Collateral Ligaments
- Bone defect
- Metal (Nickel) Allergy
1. Femoral Component
Designed & Contoured for Fixation in Distal Femur
Composition:
- Co-Cr-Mo: High strength, corrosion-resistant alloy
- Oxinium: Oxidised Zirconium exhibits exceptional wear resistance
Suitable for: Younger Population & Known Nickel Allergy
2. Tibial Component
Tibial Baseplate with Fins/Keels Contoured for Fixation in Proximal Tibia
Design: Asymmetrical (Anatomical) vs Symmetrical
Composition:
- Tivanium Alloy (Ti-6Al-4V)
- Co-Cr-Mo
3. Polyethylene Component
Specifically designed for fixation in tibial baseplate
Locking mechanism: Implant Specific
Radiolucent (Not Visible on X-Ray)
Composition:
- UHMWPE
- Vit E Doped UHMWPE
4. Bone Cement
High Viscocity Palacos Bone Cement is most commonly used
5. Patellar Component
UHMWPE with 3 peripheral lug holes for fixation in Re-surfaced Patella
Pre-Operative Evaluation
Preparation for Surgery
1. Medical Evaluation:
Medical assessment
will be conducted to evaluate your overall health.
The purpose is to
identify any existing medical comorbidity that can adversely influence with
the surgery or recovery.
Special attention needs to be focused on Comorbidities like:
Diabetes
Ischaemic Heart Disease (Prior Infarction /
Angioplasty)
Cardiac Arrhythmia (Pacemaker in situ)
Chronic Kidney Disease
Chronic Liver Disease
2. Medications:
Inform your surgeon
about the medications you are currently taking.
The surgeon will
provide guidance on which medications should be discontinued or can be
continued before the surgery.
Special attention needs to be focused on medications like:
Anticoagulants (Clopidogrel/ Apixaban/
Ecosprin 150)
DMARD (Folitrax, Leflunomide)
Steroids
3. Pre-Operative Tests
I. Pre-Anesthetic Evaluation:
CBC & PBS, ABO /Rh Grouping
CRP, ESR
Renal Function Panel (RFT)
Liver Function Panel (LFT)
Coagulation Panel: PT, INR, BT , CT
Glycaemic Panel: FBS, PPBS, HbA1C
Serology Panel: HBsAg, Anti HCV, HIV1&2, p24
Antigen (CMIA/CLIA)
Urine R/E
Aerobic Culture of Urine
Chest X-RAY PA View
ECG 12 Leads
2-D Echocardiography
II. Pre-Operative Planning:
Orthoscanogram of Both Lower Limb
Digital X-Ray Knee Joint:
- AP (standing wt bearing)
- Lat View
- Axial View
Color Doppler Study of Lower Limb (Reserved Indication)
4. Dental Evaluation
Dental procedures can
potentially introduce bacteria into the bloodstream.
Therefore, it is
advisable to address any significant dental issues, such as tooth
extractions or periodontal work, before knee replacement
surgery.
5. Urinary Evaluation
Individuals with a
recent or frequent history of urinary
infections should
consider a urological evaluation prior to knee replacement
surgery.
Older men with
prostate disease should also undergo a urologic evaluation
and treatment, if necessary, before the operation.
Financial Estimate
1. Cost Considerations
Understand the
financial implications of the chosen prosthesis.
Take into account the
overall cost of the procedure, including the prosthesis, hospital stay, &
allied expenses.
2. Hospital Stay and Cost
Be aware of the
expected duration of your hospital stay & associated costs.
Consider any potential
additional expenses that may arise during your stay.
3. Mediclaim Facility
If you have mediclaim
insurance coverage, contact the hospital's mediclaim department at least one
week before the surgery.
Provide them with your
policy documents and ensure all necessary procedures are followed.
Peri-Operative Protocol
Upon your admission to the hospital, a resident or registrar doctor will visit you. They will conduct general evaluation & provide a brief explanation of pre and post-operative procedures.
An Anaesthesiologist will visit you to
explain the type of anesthesia to be administered, medications that need to be
discontinued, and medications to be taken on the day of surgery. You will be
instructed for NBM (to refrain from eating or drinking) for at least 6-8 hours
before the surgery.
Dr. Sanyal will visit you at evening, explaining you in detail about the procedure. He will perform a final clinical evaluation & cross check his pre operative planning. The OT timing, Implant & other relevant issues will also be reiterated by him.
Prior to surgery, you will be asked to bathe with Avaguard Solution on the night
before the procedure and a few hours before it, ensuring cleanliness of your
body and the surgical site.
Usually 1 -2 units of PCV are reserved prior to surgery as a exigency measure for anticipated blood loss. Majority of patients do not require post operative blood transfusion.
Surgical Procedure for Total Hip Replacemnet
1. Anesthesia
- You will be transferred to OR at the appointed hours of surgery. The anesthesia team
will
establish IV access & administer IV antibiotics & other pre-anesthetic medication.
- Majority of cases of Knee Replacement are performed under Spinal/Epidural Anaesthesia
where patient retain their consciousness but feel numb below waist.
- In reserved indications General Anesthesia needs to be administered. Choice of
anaesthesia is absolute discretion of the Anaesthesia team.
2. Positioning & Draping
- After Anaesthesia patient positioning is done & Pneumatic Torniquet is
applied over thigh of operating limb.
- Thorough cleansing of the operative limb from flank to toes is performed using
10%
Betadine solution & 2% Sterilium.
- Draping of the operative limb is performed using Hallyard Draping Sheet, Hip U
Drape, Sterile Stockinette & IOBAN.
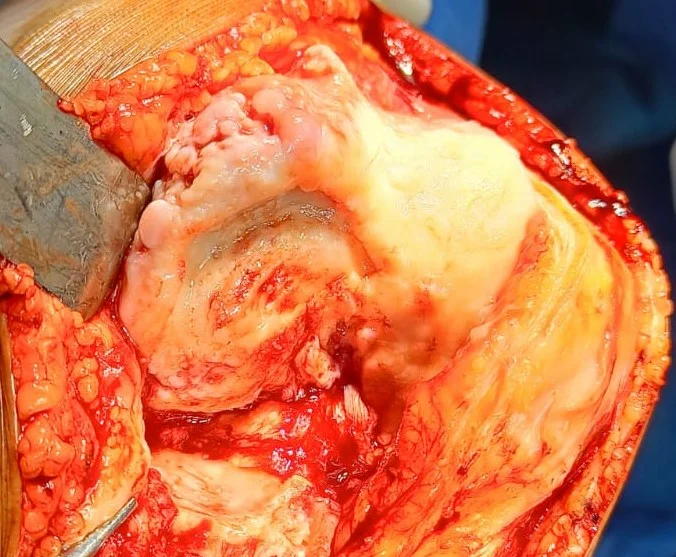
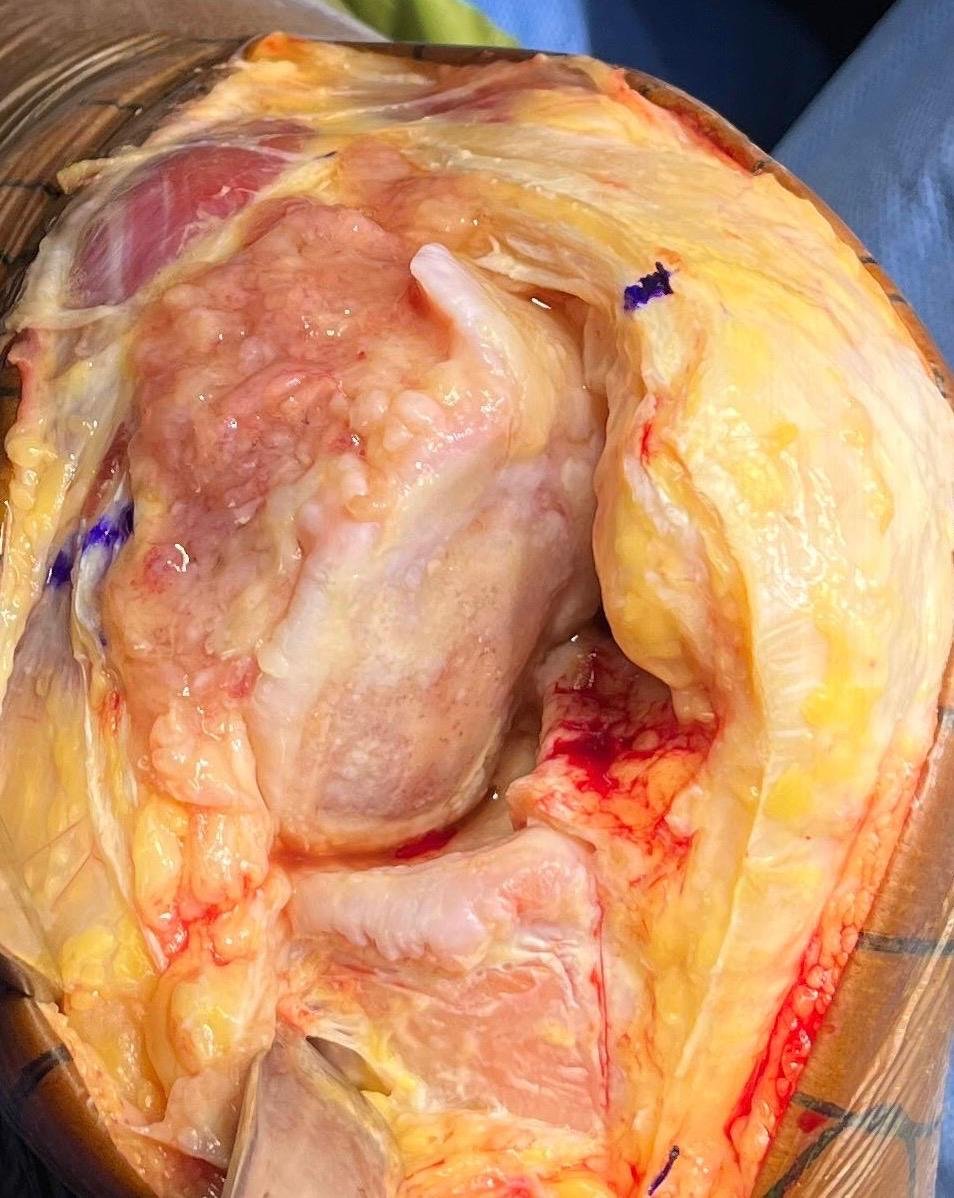
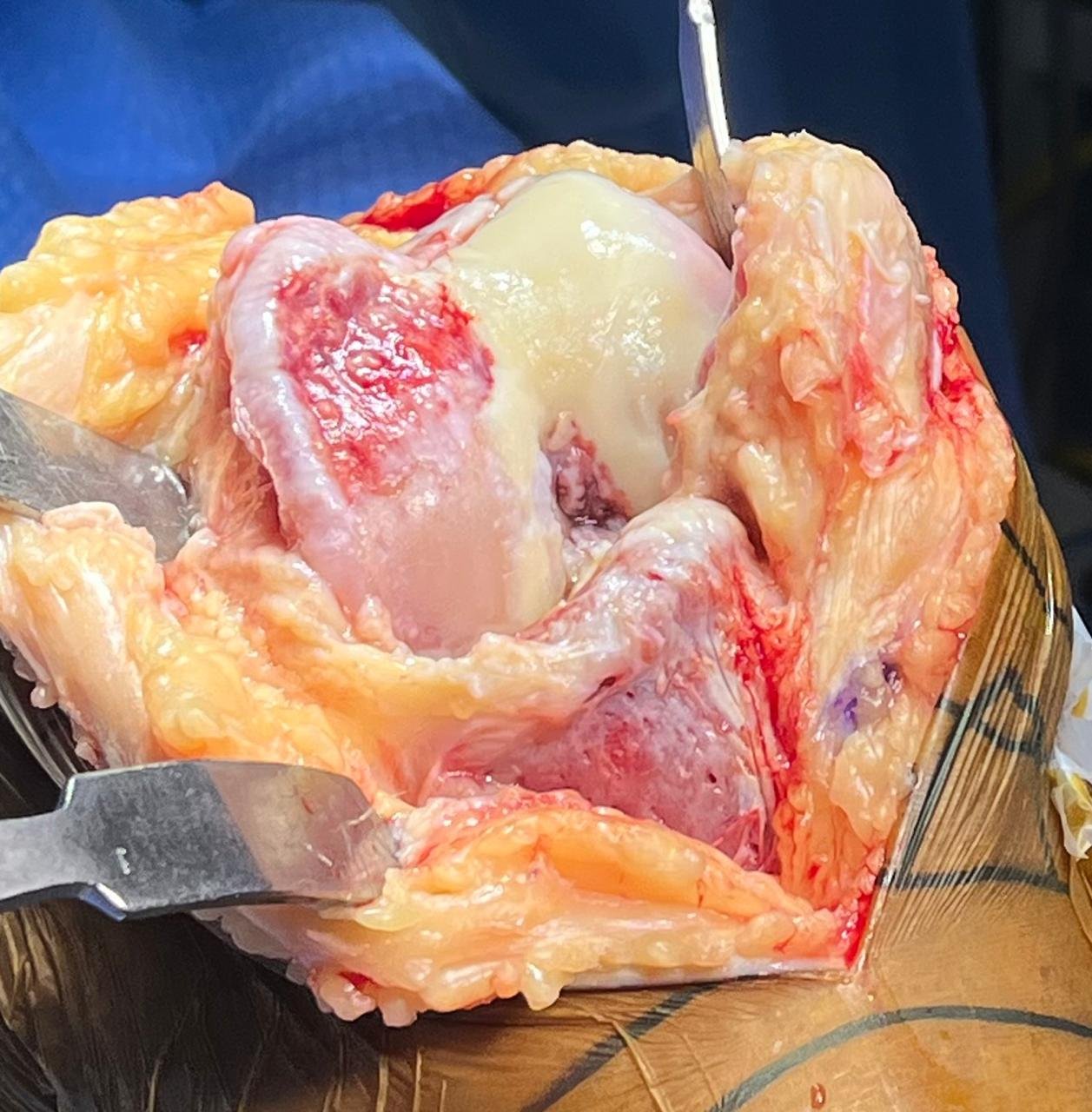
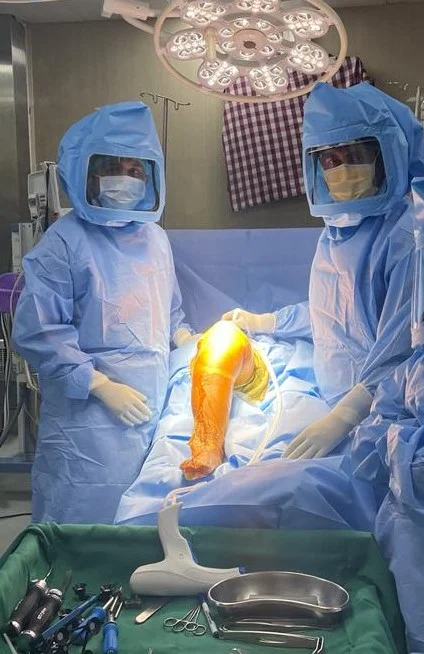
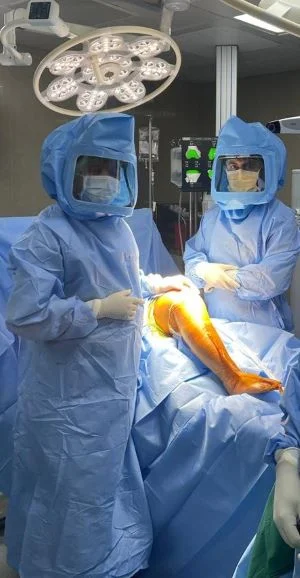
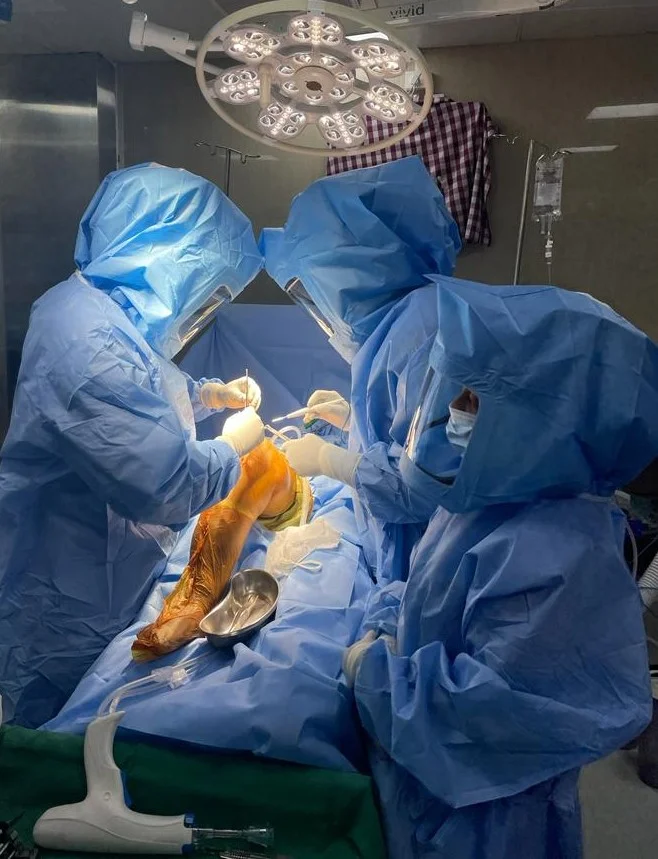
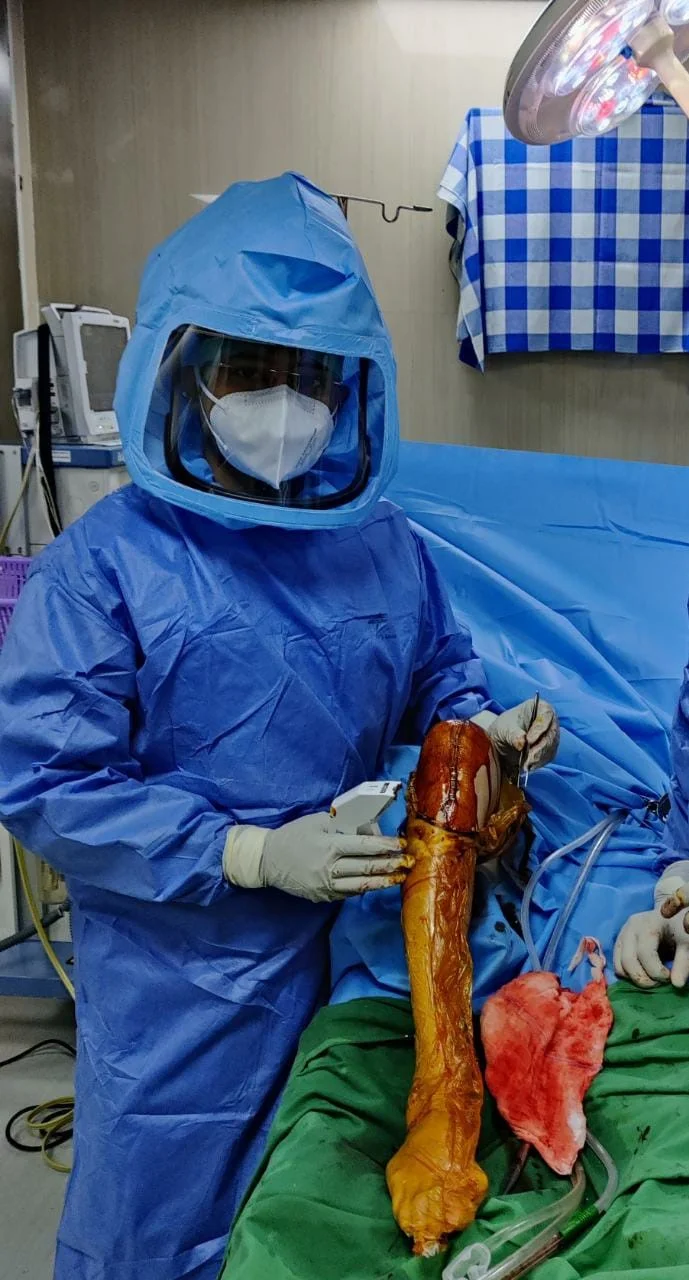
3. Surgery
Usual duration of surgery is 90-100 mins. The surgery principally aims at precise measured
resection of eroded cartilage & bone of knee joint, correction of deformity, appropriate
balancing of soft tissue.
The prosthesis is implanted to cut surface of distal femur & proximal tibia with specifically
designated bone cement.
Cocktail infiltration is given locally intra-operatively to reduce post operative pain. Wound
is closed in layers using absorbable sutures & skin with staplers.
Occlusive dressing with compression bandage & stockinettes are applied.
4. Post surgery
Patient will be shifted to OR recovery room where he/she will undergo observation for another
1-2 hours. Later on patient will be shifted to ward.
Patients are allowed to have clear fluid & liquid 4 hours after surgery & semi-solid diet at
night.
Hospital Stay and Recovery
Your hospital stay typically lasts 4 to 5 days.
Analgesic medications (Parenteral & Oral) will be administered appropriately weighing the existing
co-morbidity.
Day 1 After Surgery
- Transdermal analgesic skin patch will be applied.
- A compression bandage which had been applied over sterile dressing will be removed.
- Ambulation with walker (PWB) under assistance from a physiotherapist.
- CBC & RFT.
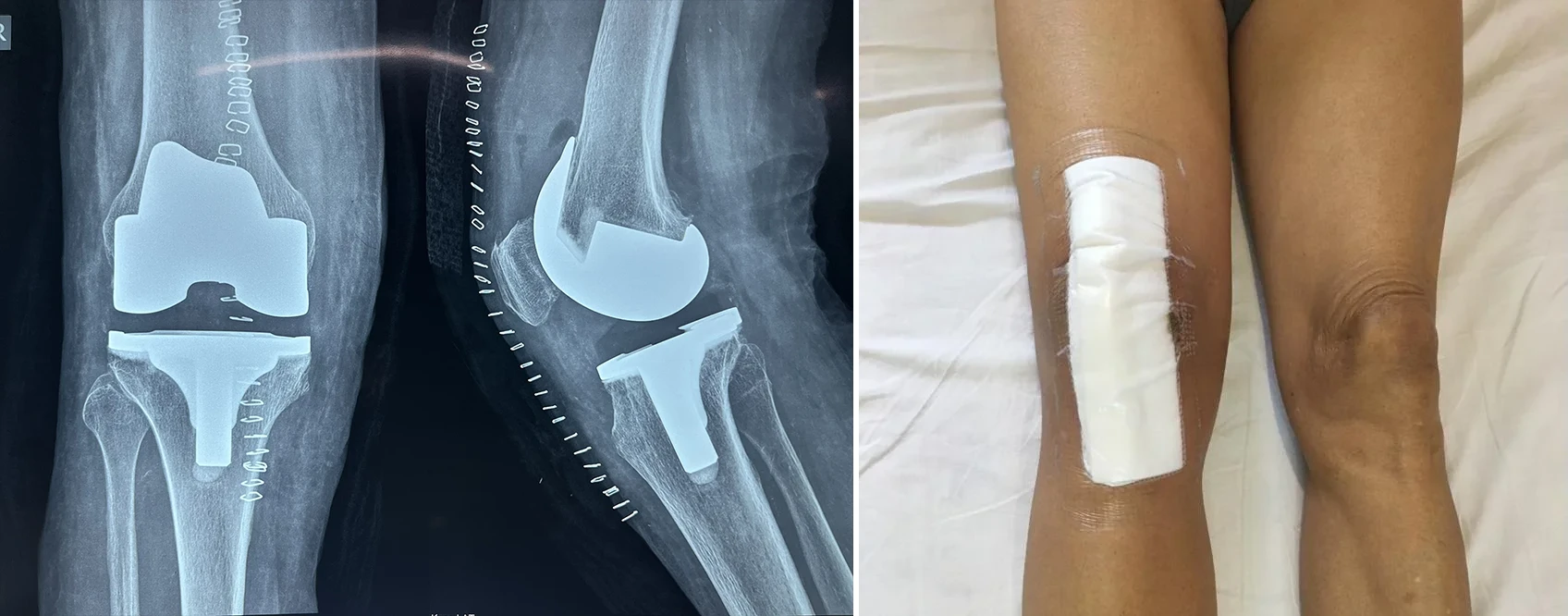
Day 2 After Surgery
- Dressing change.
- Post-op x-ray.
- Continuation of physiotherapy (Knee Muscle Strengthening, ROM).
Day 3 After Surgery
- Chair transfer, commode training, staircase climbing.
- Discharge on Day 3 afternoon.
How to care After Your Total Hip Replacement Surgery?
- Your surgical wound will have staples that will be removed around 14
days post surgery.
- Sponging of body is allowed but avoid bathing till wound is healed (4-5
days after staples removal).
- Surgical wound will be covered with occlusive dressing. Do not change
dressing at home.
- Exercise is the most critical component of home care, particularly
during the first 4-6 weeks post surgery.
- Daily 30-45 mins dedicated exercise under supervision of a trained
physiotherapist.
- Strengthening of thigh & calf muscle to improve endurance & regain
muscle strength.
- ROM exercises & specific activity programme.
- Loss of appetite & alteration of bowel habits are quite common post
surgery.
- Maintain a balanced diet with adequate protein intake to ensure proper
tissue healing & regain muscle strength.
- Ensure proper hydration by consuming ample fluids.
- Use a walker for the first 1 month until you improve your balance,
flexibility & strength.
- Stairs are of particular concern. Always have someone beside you during
staircase ascend/descend. (Up with Good, Down with Bad).
- Continue usage of stockinettes for 1 month post surgery.
- Active ankle pump exercise.
- Oral anticoagulant (Xarelto 10 mg / Eliquis 2.5) 35 days post surgery.